Scabies is a skin condition that is caused by scabies mites. Scabies mites are tiny bugs that burrow, lay eggs, and live underneath the skin.
What causes scabies? Scabies is spread through close and prolonged contact with a person who has scabies. This includes having sex, sleeping in the same bed, or sharing towels or clothing. Scabies spreads quickly and must be treated as soon as it is found.
What are the signs and symptoms of scabies?
Most people do not know they have scabies until a few weeks after mites are under the skin. Scabies mites are too small to be seen on your body.
See a healthcare provider if the following symptoms:
- Red, raised bumps or burrow marks that appear on and between your fingers, wrists, ankles, elbows, groin, armpits, and breasts.
- Intense itching that is worse at night.
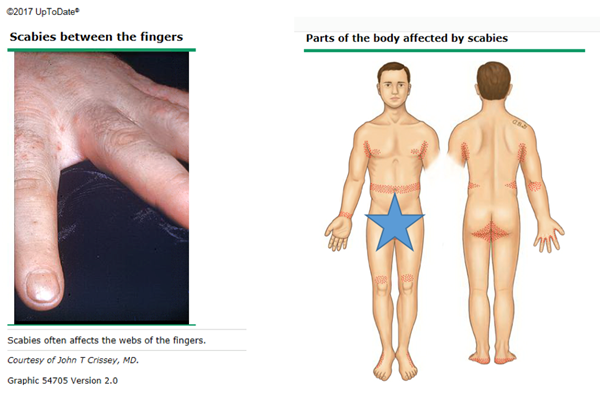
How is scabies treated?
There is more than one medicine cream that may be used to treat scabies. Always read the directions and follow your caregiver’s directions for scabies medicines.
- Rub a thin layer of the medicine onto your entire body from the neck down.
- Leave the cream on the amount of time that is required for the medicine you are using. This may be between 8 to 14 hours.
- Take a bath or shower to wash all medicine from the skin after the scabies treatment is over.
- Put on clean clothes after you have rinsed the medicine off. You may need another scabies treatment in about 7 to 10 days if you continue to have symptoms.
How do I prevent the spread of scabies?
- Tell all sex partners and anyone who has shared your clothing or bed for the past month about the scabies.
- Take or apply over-the-counter and prescription medicines as told by your health care provider.
- Apply medicated cream or lotion as told by your health care provider.
- Do not wash off the medicated cream or lotion until the necessary amount of time has passed.
- Avoid scratching your affected skin-could cause an infection.
- Keep your fingernails closely trimmed to reduce injury from scratching.
- Take cool baths or apply cool washcloths to help reduce itching.
- Clean all items that you recently had contact with, including bedding, clothing, and furniture. Do this on the same day that your treatment starts.
- Use hot water when you wash items.
- Place un-washable items into closed, airtight plastic bags for at least 3 days. The mites cannot live for more than 3 days away from human skin.
- Vacuum furniture and mattresses that you use.
- Make sure that other people who may have been infested are examined by a health care provider. These include members of your household and anyone who may have had contact with infested items.
- Do not have close body contact with anyone until scabies mites are gone.
Contact your caregiver?
- The bites become filled with pus or crusty.
- The itching gets worse after the scabies treatment.
- You have new bite or burrow marks after your treatment.
- You become dizzy, nauseous, or vomit after using medicine to treat scabies.
- You develop a fever and red, swollen, painful areas on your skin.
More Information can be found on the Center for Disease Control website.
Source: Mosby Patient Education and Uptodate
